Explore picrust2 profile
Source:vignettes/Explore_picrust2_profile.Rmd
Explore_picrust2_profile.RmdFirst, load the rbims package.
The second thing to do would be to read the KO_picrust2_data. The meta file is a tab-separated file containing the name of your ids (bins or sites) and any extra information you would like to use for visualization.
Read metadata
The metadata table can be read in various formats (csv, tsv, txt, xlsx); you will need to use the corresponding function to read the type of file you have. meta and try.
The example data is from an article already published link and were sediment core samples that were collected from three zones of mangrove ecosystem: Basin, Fringe and Impaired. The samples were taken during two seasonal conditions, dry and flood seasons, at three sediment depths: surface (5), mid-layer(20), and deeper sediment layers (40), to assess the impact of degradation level or zone, seasonal variation, and sediment depth on microbial communities.
library(readr)
meta<-read_tsv("../inst/extdata/Metadatos-MANGLAR")
#> Rows: 53 Columns: 10
#> ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> Delimiter: "\t"
#> chr (8): Bin_name, lat, coll_date, ID, seqR2, zone, month, season
#> dbl (2): long, depth
#>
#> ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
#> ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
head(meta)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 10
#> Bin_name lat long coll_date ID seqR2 zone month season depth
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 zr2502_10_R1 18.65135 -91.8 30/5/2018 P10 zr2502_1… Basin May Dry 5
#> 2 zr2502_43_R1 18.65135 -91.8 30/5/2018 P43 zr2502_4… Basin May Dry 5
#> 3 zr2502_8_R1 18.65135 -91.8 30/5/2018 P8 zr2502_8… Basin May Dry 5
#> 4 zr2502_21_R1 18.65135 -91.8 17/1/2018 P21 zr2502_2… Basin Jan Flood 5
#> 5 zr2502_4_R1 18.65135 -91.8 17/1/2018 P4 zr2502_4… Basin Jan Flood 5
#> 6 zr2502_5_R1 18.65135 -91.8 17/1/2018 P5 zr2502_5… Basin Jan Flood 5Let’s chaghe the names of ids for visualization purposes:
library(dplyr)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'dplyr'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
library(stringr)
meta <- meta %>%
mutate(
Bin_name = str_extract(Bin_name, "(?<=zr2502_)(\\d+)(?=_R1)")
)
head(meta)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 10
#> Bin_name lat long coll_date ID seqR2 zone month season depth
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 10 18.65135 -91.8 30/5/2018 P10 zr2502_10_R2 Basin May Dry 5
#> 2 43 18.65135 -91.8 30/5/2018 P43 zr2502_43_R2 Basin May Dry 5
#> 3 8 18.65135 -91.8 30/5/2018 P8 zr2502_8_R2 Basin May Dry 5
#> 4 21 18.65135 -91.8 17/1/2018 P21 zr2502_21_R2 Basin Jan Flood 5
#> 5 4 18.65135 -91.8 17/1/2018 P4 zr2502_4_R2 Basin Jan Flood 5
#> 6 5 18.65135 -91.8 17/1/2018 P5 zr2502_5_R2 Basin Jan Flood 5Let’s read again the KO_picrust2 data setting profile=F.
KO_picrust2_profile_long <- read_picrust2("../inst/extdata/KO_metagenome_out/KO_pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv",
database = "KO",
profile = F)
head(KO_picrust2_profile_long)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> KO Bin_name Abundance
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 K00001 zr2502_1_R1 82
#> 2 K00001 zr2502_10_R1 407
#> 3 K00001 zr2502_11_R1 0
#> 4 K00001 zr2502_12_R1 243
#> 5 K00001 zr2502_13_R1 0
#> 6 K00001 zr2502_14_R1 184The same change in Bin names:
KO_picrust2_profile_long <- KO_picrust2_profile_long %>%
mutate(
Bin_name = str_extract(Bin_name, "(?<=zr2502_)(\\d+)(?=_R1)")
)
head(KO_picrust2_profile_long)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> KO Bin_name Abundance
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 K00001 1 82
#> 2 K00001 10 407
#> 3 K00001 11 0
#> 4 K00001 12 243
#> 5 K00001 13 0
#> 6 K00001 14 184Map to the KEGG database
Then map the KO to the rest of the features of the KEGG and rbims database.
ko_bin_mapp<-mapping_ko(KO_picrust2_profile_long)Metabolism subsetting
In this example, we will use energy metabolism to explore the rest of the functions.
- Create a vector with the metabolism of interest.
Other_energy<-c("Fermentation", "Carbon fixation", "Methane metabolism",
"Sulfur metabolism", "Nitrogen metabolism")- Use get_subset_pathway to subset the table using the cycles and the information of the energy metabolism.
library(tidyr)
Energy_metabolisms<-ko_bin_mapp %>%
drop_na(Cycle, Pathway_cycle) %>%
get_subset_pathway(Cycle, Other_energy)- Plot the information using the plot_heatmap function. The argument order_y will order the rows according to a metabolic feature; in this case, we order the pathways_cycle according to cycle.
plot_heatmap(tibble_ko=Energy_metabolisms,
y_axis=Pathway_cycle,
order_y = Cycle,
split_y = TRUE,
data_experiment = meta,
order_x = "zone",
analysis = "KEGG",
calc="Percentage")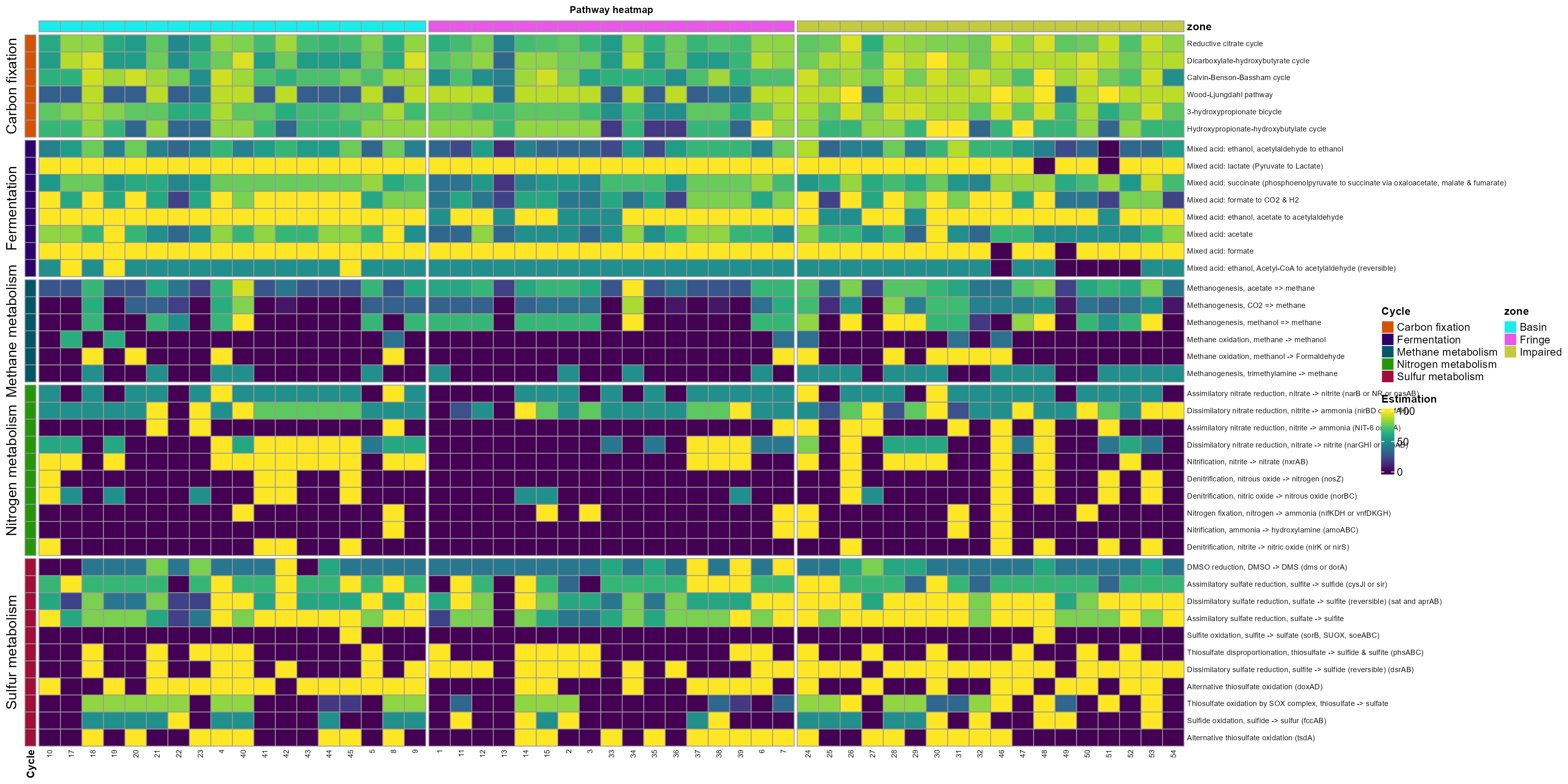
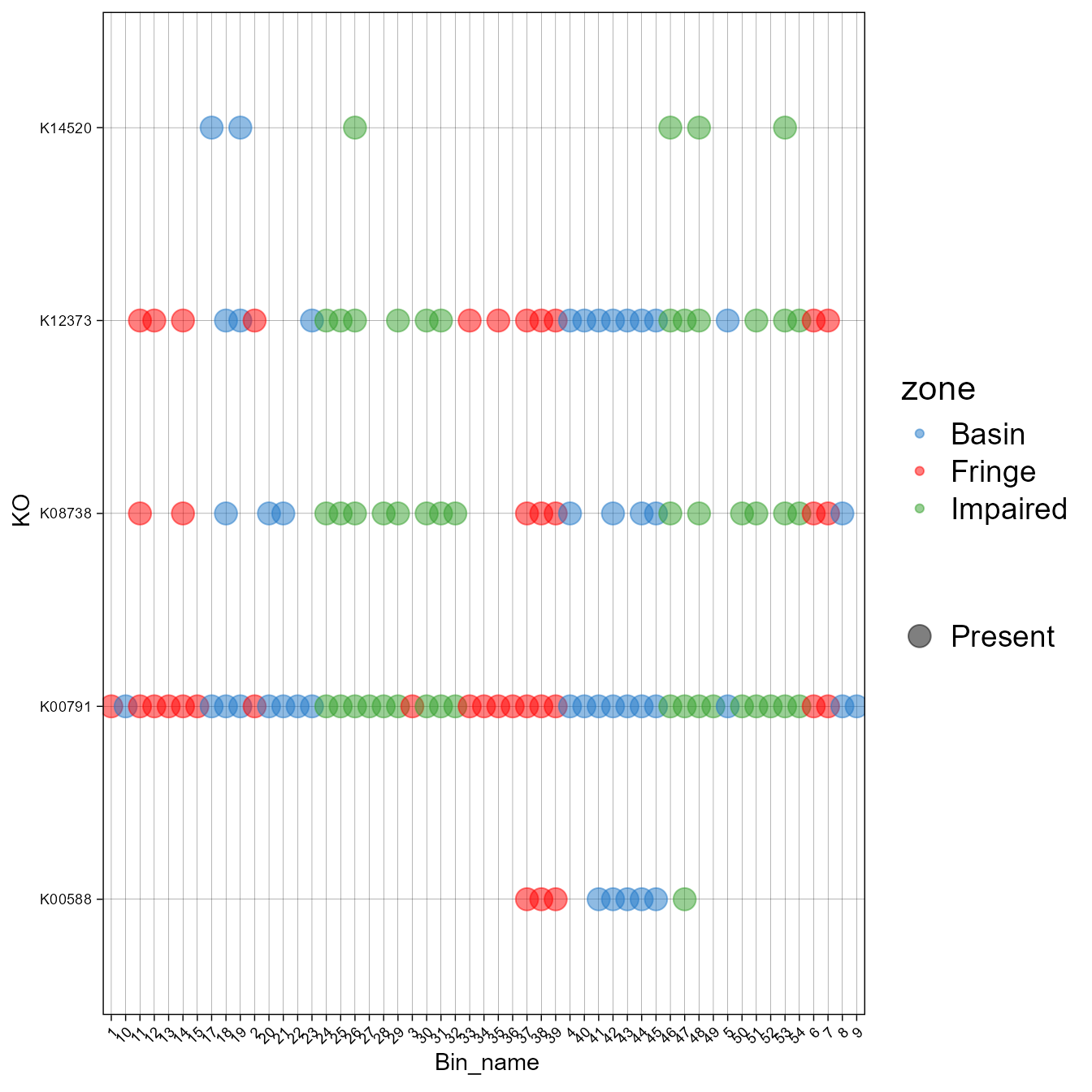
Example of exploring a specific KEGG pathway
specific<-c("map05416", "map00363", "map00604", "map00908", "map00941")- Now, let’s extract the profile associated with that metabolic pathway.
library(tidyr)
specific_subset<-ko_bin_mapp%>%
drop_na(Pathway) %>%
get_subset_pathway(Pathway, specific)
head(specific_subset)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 66
#> Module Module_description Pathway Pathway_description Cycle Pathway_cycle
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 M00039 Monolignol biosynthesi… map009… Flavonoid biosynth… NA NA
#> 2 NA NA map009… Zeatin biosynthesis NA NA
#> 3 NA NA map054… Viral myocarditis NA NA
#> 4 M00079 Keratan sulfate degrad… map006… Glycosphingolipid … NA NA
#> 5 NA NA map003… Bisphenol degradat… NA NA
#> # ℹ 60 more variables: Detail_cycle <chr>, Genes <chr>, Gene_description <chr>,
#> # Enzyme <chr>, KO <chr>, rbims_pathway <chr>, rbims_sub_pathway <chr>,
#> # `1` <dbl>, `10` <dbl>, `11` <dbl>, `12` <dbl>, `13` <dbl>, `14` <dbl>,
#> # `15` <dbl>, `17` <dbl>, `18` <dbl>, `19` <dbl>, `2` <dbl>, `20` <dbl>,
#> # `21` <dbl>, `22` <dbl>, `23` <dbl>, `24` <dbl>, `25` <dbl>, `26` <dbl>,
#> # `27` <dbl>, `28` <dbl>, `29` <dbl>, `3` <dbl>, `30` <dbl>, `31` <dbl>,
#> # `32` <dbl>, `33` <dbl>, `34` <dbl>, `35` <dbl>, `36` <dbl>, `37` <dbl>, …- Now, let’s create a plot of the presence and absence of the different KO associated with that pathway. Besides presence and absence, it is possible to plot abundance or the percentage of genes within certain pathways (See plot_bubble, calc argument).
plot_bubble(tibble_ko = specific_subset,
x_axis = Bin_name,
y_axis = KO,
analysis="KEGG",
data_experiment = meta,
color_character = zone,
calc="Binary",
range_size = c(1,10))